how to find electron affinity|8.4: Electron Affinity : Bacolod Electron affinity is defined as the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative . The Official Habesha Sports Betting YouTube Channel. ትክክለኛው የሐበሻ ስፖርት ውርርድ YouTube ቻንላችንን ይቀላቀሉ::ከሐሰተኛና ተመሣሣይ .
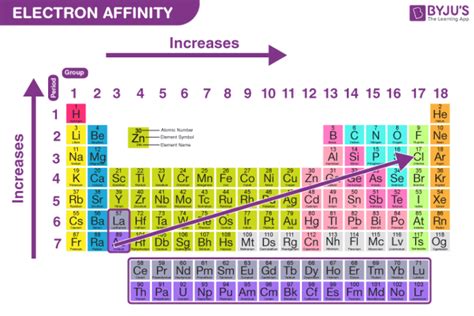
how to find electron affinity,Learn what electron affinity is, how it varies across the periodic table, and how to calculate it using the Born-Haber cycle. Find out the factors affecting electron affinity, the electron affinity of halogens, and the difference between electron affinity and ionization potential. Tingnan ang higit paElectron affinity is defined as The electron affinity is the potential energy change of the atom when an electron is added to a neutral gaseous atomto form a negative ion. So the more negative the electron affinity the more favourable the electron addition . Tingnan ang higit paThe amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form an anion is called electron affinity. Electron affinities . Tingnan ang higit pahow to find electron affinityThe general factors that affect electron affinity are listed below. 1. \(\begin{array}{l}Electron\ affinity = \frac{1}{Atomic\ Size}\end{array} \) 2. \(\begin{array}{l}Electron\ affinity = Effective\ Nuclear\ Charge\end{array} \) 3. \(\begin{array}{l}Electron\ . Tingnan ang higit pa Electron affinity is defined as the change in energy (in kJ/mole) of a neutral atom (in the gaseous phase) when an electron is added to the atom to form a negative .
The electron affinity (Eea) of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron attaches to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form an anion. X(g) + e → X (g) + energyThis differs by sign from the energy change of electron capture ionization. The electron affinity is positive when energy is released on electron capture.
The electron affinity ( EA E A) of an element E E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: E(g) +e− → E−(g) energy .Learn what electron affinity is and how it is measured for group 6 and 7 elements. Find out how nuclear charge, distance and screening affect the energy released when atoms gain .Learn how to find electron affinity using the Born-Haber cycle and the periodic table. See the chemical equation, the trend across a period and down a group, and the exceptions and examples of electron affinity.
Learn what electron affinity is, how it differs from electronegativity and ionization energy, and how it varies across the periodic table. Explore the effects of atomic size, nuclear charge, shielding and repulsion on .
Learn what electron affinity is, how to measure it, and how it varies on the periodic table. Find out the highest and lowest electron affinity values, and the difference .Electron affinity is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. For many atoms, electron affinity is exothermic. Skip to content Watch a video explaining how electron affinity varies across the periodic table and why it matters for chemistry. Khan Academy offers free, high-quality education .What is Electron Affinity. The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released per mole when an electron is added to a neutral atom. It is the opposite of ionization energy [1-4]. How to Find Electron Affinity. .
What is Electron Affinity? Chemists define electron affinity as the change in energy, measured in units of kJ/mole, experienced when an electron is added to a gaseous atom. This process creates a negative . Electron Affinity is the amount of energy RELEASED when you add an electron to a particle in the gas phase. So the general equation is:A + electron = A(-) + . Electron affinity is a measure of how much an atom wants to gain an electron, becoming an anion. Unfortunately 2 different definitions are used: intro textbooks use 1 definition and everyone else uses the other! I think you should use the standard advanced definition, according to which electron affinity EA = IE 0, the energy of this .

The first ionization energy for sodium is one and one-half times larger than the electron affinity for chlorine. Na: 1st IE = 495.8 kJ/mol. Cl: EA = 328.8 kJ/mol. Thus, it takes more energy to remove an electron from a neutral sodium atom than is given off when the electron is picked up by a neutral chlorine atom. Electron affinity is a measure of how readily a neutral atom gains an electron. Electron affinity (E ea) is the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom in the gas phase. In simple terms, it is a measure of a neutral atom’s ability to gain an electron. Electron Affinities. Electron affinity, often abbreviated as EA, is the energy released when an electron is added to a valence shell of the atom. F(g) + e - -> F-(g) EA = -328 kJ/mol [When an electron is added to an atom, energy is .8.4: Electron Affinity The electron affinity is defined as the amount of energy released when an electron is added to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state to form a negative ion \[X_{(g)} + e^− \rightarrow X^−_{(g)} + energy\] Z Element Name Electron affinity (eV) Electron affinity (kJ/mol) 1: 2 D: Deuterium: 0.754 59(8) 72.807(8) 1: 1 H: This chemistry tutorial describes the concept of electron affinity and covers the general periodic trend of electron affinity along with notable exceptions i.
Electron Affinities of the Main-Group Elements* The electron affinity is a measure of the energy change when an electron is added to a neutral atom to form a negative ion. For example, when a neutral chlorine atom in the gaseous form picks up an electron to form a Cl- ion, it releases an energy of 349 kJ/mol or 3.6 eV/atom. Definition of electron affinity Electron affinity is the affinity of an element to an electron. This is measured by the energy released when an element in its gaseous state accepts an electron to form an anion. So this is an exothermic reaction. They are expressed in KJ mol-1.
Electron Affinity. The electron affinity (EA) of an element E is defined as the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom or ion: [latex]E_{(g)}+e^- \rightarrow E^-_{(g)} \;\;\; \text{energy .
The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative electron affinities (the highest affinity .
Electron affinity is defined as the quantitative measurement of the energy change that results from adding a new electron to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous state. The more negative the electron affinity value, the higher an atom’s affinity for electrons.The energy of an atom is stated when an atom loses or gains energy .
The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative electron affinities (the highest affinity for an added electron) are those with the smallest size and highest ionization energies and are located in the upper right .Electron Affinity of Noble Gases. Next to the right, we have the noble gases which are characterized by endothermic electron affinity because there are no vacant p orbitals in their valence shell, not even with one electron in it, and they do not “want” to add an electron to higher energy orbitals: Electron Affinity in Groups 1A, 2A, and 3A .
how to find electron affinity 8.4: Electron Affinity The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the energy change that occurs when an electron is added to a gaseous atom to give an anion. In general, elements with the most negative electron affinities (the highest affinity for an added electron) are those with the smallest size and highest ionization energies and are located in the upper right .

Chemical bonding - Electron Affinity, Intermolecular Forces, Covalent Bonds: Third in importance for bond formation after size and ionization energy is the energy change accompanying the attachment of electrons to a neutral atom. This energy is expressed as the electron affinity, which is the energy released when an electron is .
how to find electron affinity|8.4: Electron Affinity
PH0 · electron affinity
PH1 · What is Electron Affinity?
PH2 · What Is Electron Affinity?
PH3 · Khan Academy
PH4 · Electron affinity
PH5 · Electron Affinity: Definition, Chart & Trend in Periodic Table
PH6 · Electron Affinity: Definition, Chart & Trend in Periodic
PH7 · Electron Affinity Trend and Definition
PH8 · Electron Affinity
PH9 · 8.4: Electron Affinity
PH10 · 7.5: Electron Affinities